- Published on
INT8 Quantization Basics
- Authors

- Name
- Rand Xie
- @Randxie29
Reducing serving latencies on edge devices have always been a popular topic for edge ML. In this post, I will go into INT8 quantization, a seemly weird but effective quantization techniques to largely improve neural networks' inference speed. The main idea of quantization is to improve speed by representing weigths in lower precision (e.g. float16, int8, while training uses float32). At the same, we target at minimizing the loss of accuracies.
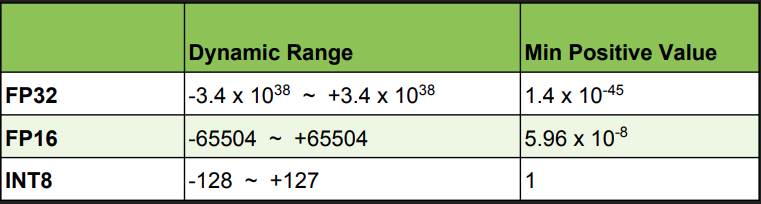
One big challenge for representing weights using lower precision is the smaller numerical range an INT8 can represent, as shown below:
Luckily, neural networks' weights do not require the full range. For example, here's the weight distribution of efficientnet (script to plot)
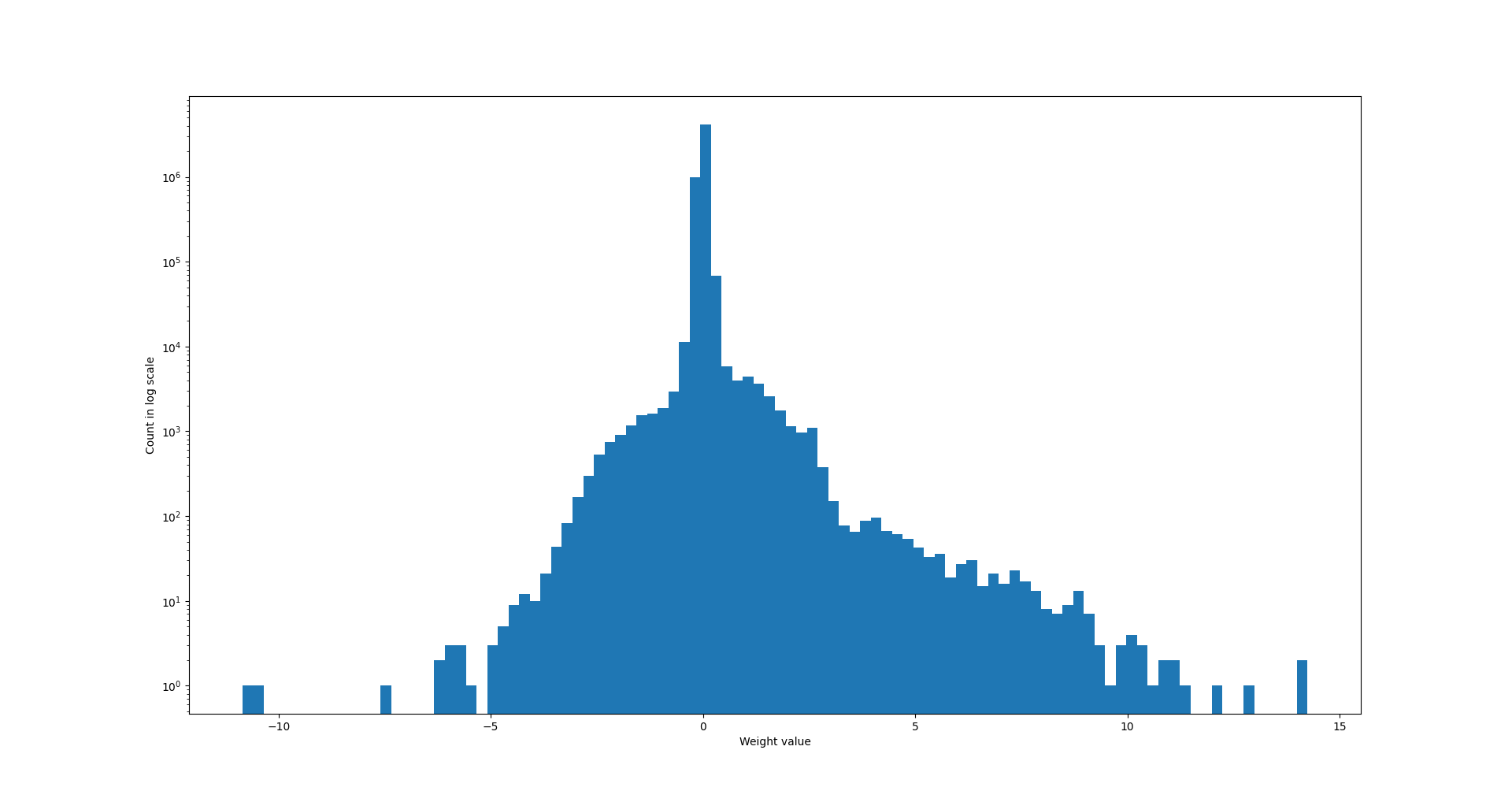
As we can see, the maximum absolute weigth value is less than 20, and most values are concentrated around 0. In other words, we don't need the full numerical range of float to represent neural network weights. To quantize weights, we will create a mapping from INT8 to float32:
,
where R is the actual weight in float 32, Q is the quantized weight, S is the scaling factor and Z is the zero point.
Post-training quantization v.s. Quantization-aware Training
When talked about quantization techniques, we can generally categorize them into post-training quantization and quantization-aware training:
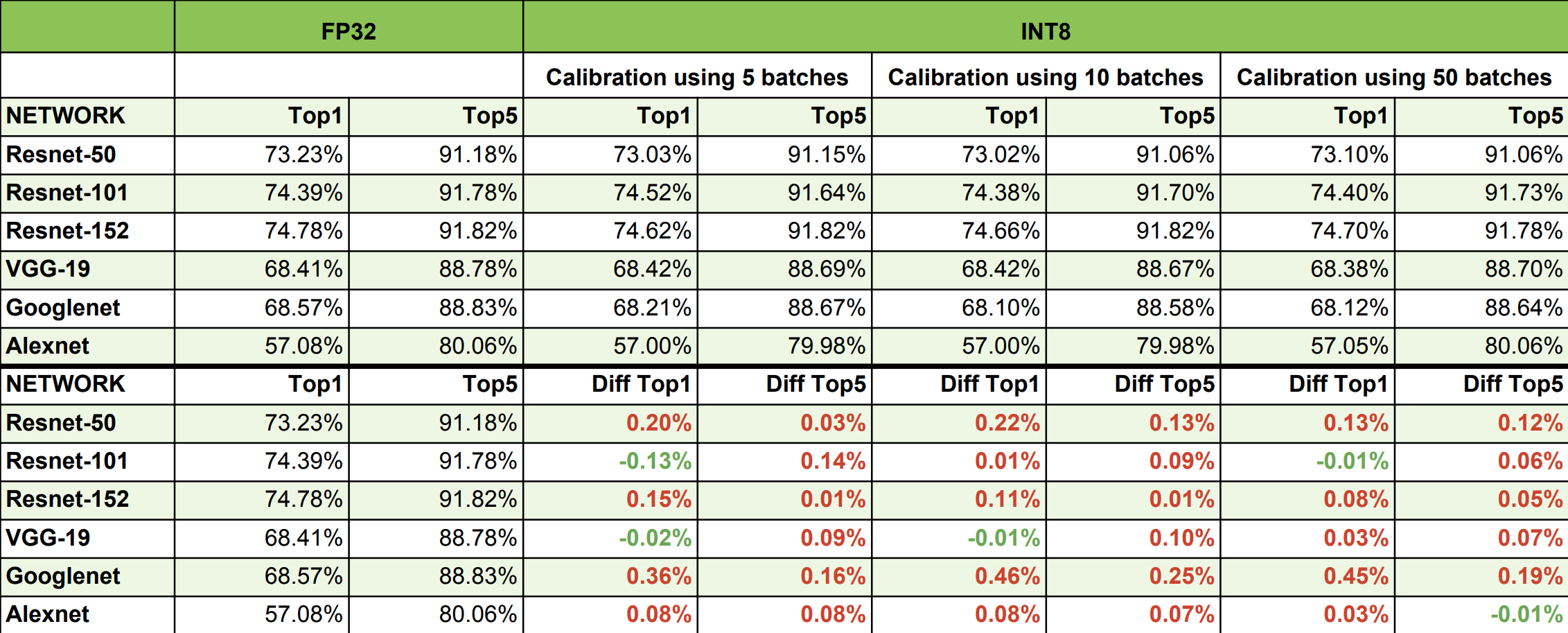
Post training quantization uses a calibration dataset to compute the quantization factors (scaling factor and zero point). It does not require re-training and is easier to integrate into the original ML workflow. TensorRT adopts post training quantization to compute quantization factors for each layer, and uses KL divergence as the optimization metric. The below table shows accuracy drop with INT8 quantization.
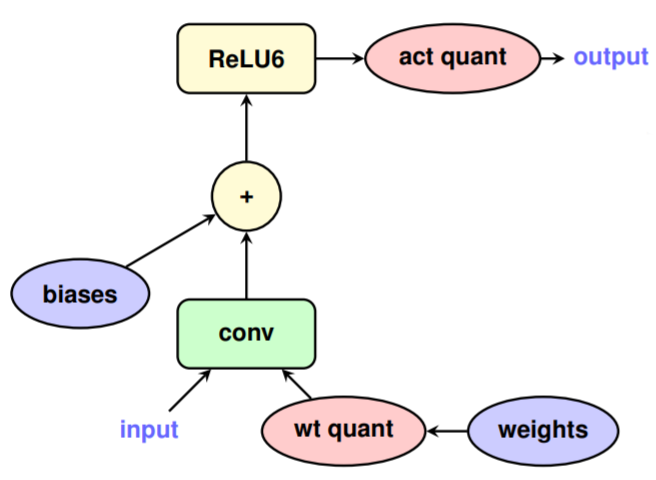
Quantization aware training, as its name suggesting, tries to quantize the weight during training. As expected, it's more invasive to the original training pipeline. On the other hand, we can expect less accuracy drop. Tensorflow supports quantization aware training by placing quantization emulation operations [2].
For more quantization techniques, the reference [3] is a good survey on neural network quantization. I would encourage researchers/engineers who are working on edge ML to take a look.
Reference: